Dog behavior: Understanding body language
Dog behavior is intensely influenced by body language. If the dog wants to communicate with other dogs or humans, he sends appropriate signals through his body. Learn to read these signs to understand your dog better.
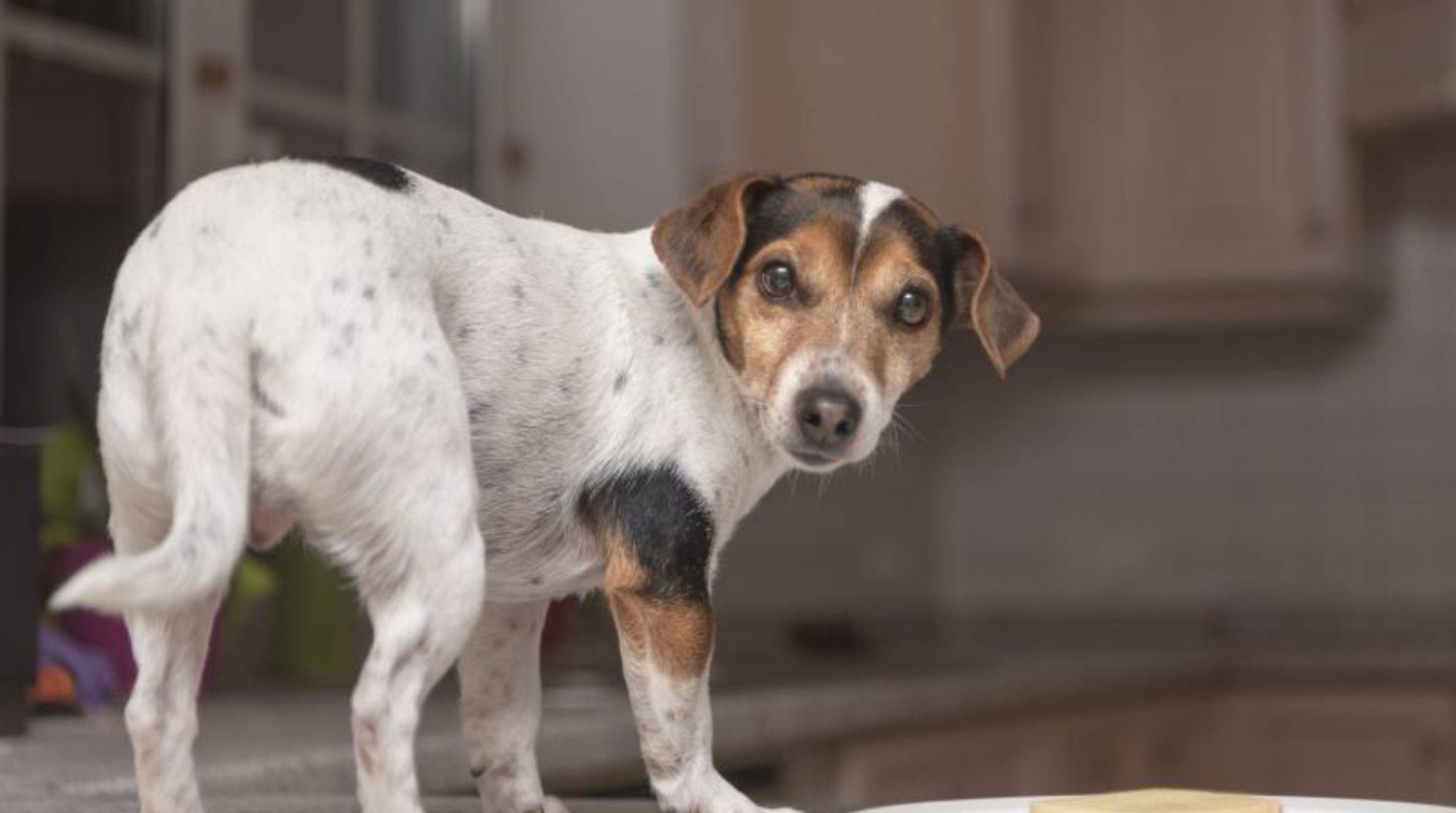
Dogs don’t just bark and growl: Dog behavior toward conspecifics, like humans, can be inferred through verbal expressions and body language. If you pay attention to rod position and body posture, it will be easier to understand what your dog wants to tell you.
The rod position: Signal antenna of the body language
The posture of the tail – the dog’s tail – can already tell you a lot about the dog’s behavior because not every dog that wags its seat is in a friendly mood. A wagging with the tail expresses over the body language primarily a state of excitement. This can, of course, be joyful anticipation, but it can also be a sign of restlessness or an aggressive form. You will know the exact meaning of tail wagging when you read it in the context of general dog behavior.
Playing posture: body language for fetching sticks
If your dog wants to play, he stretches his front legs long in front of him. The chest almost touches the ground in this posture, while the hind legs are upright and the tail wags vigorously. To do this, the dog may bark or whine about, prompting you to throw sticks or play ball.
Threatening posture: dog behavior that requires caution
The tail is also steeply up when the dog is in a threatening posture. The body posture is upright because the dog wants to impress his opponent through body language alone. The ears are erect, and the facial expressions are tense – a threatening facial expression almost like humans. The dog growls and may also raise its flews as a threat sign. Now extreme caution is required; you should not underestimate these signs.
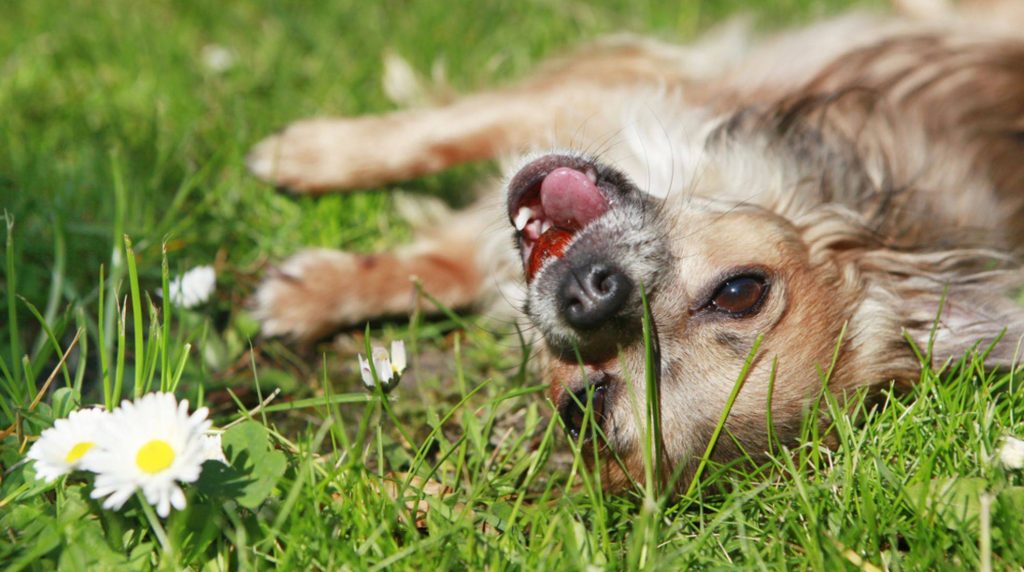
The dog is afraid: Fearful body language.
If a dog is afraid, he makes his back round and curls up inside himself. He pulls in his tail, tries to make himself small, and dodge backward. This form of dog behavior is often accompanied by nervous whining or squealing.
Your dog’s facial expressions: Body language at a glance
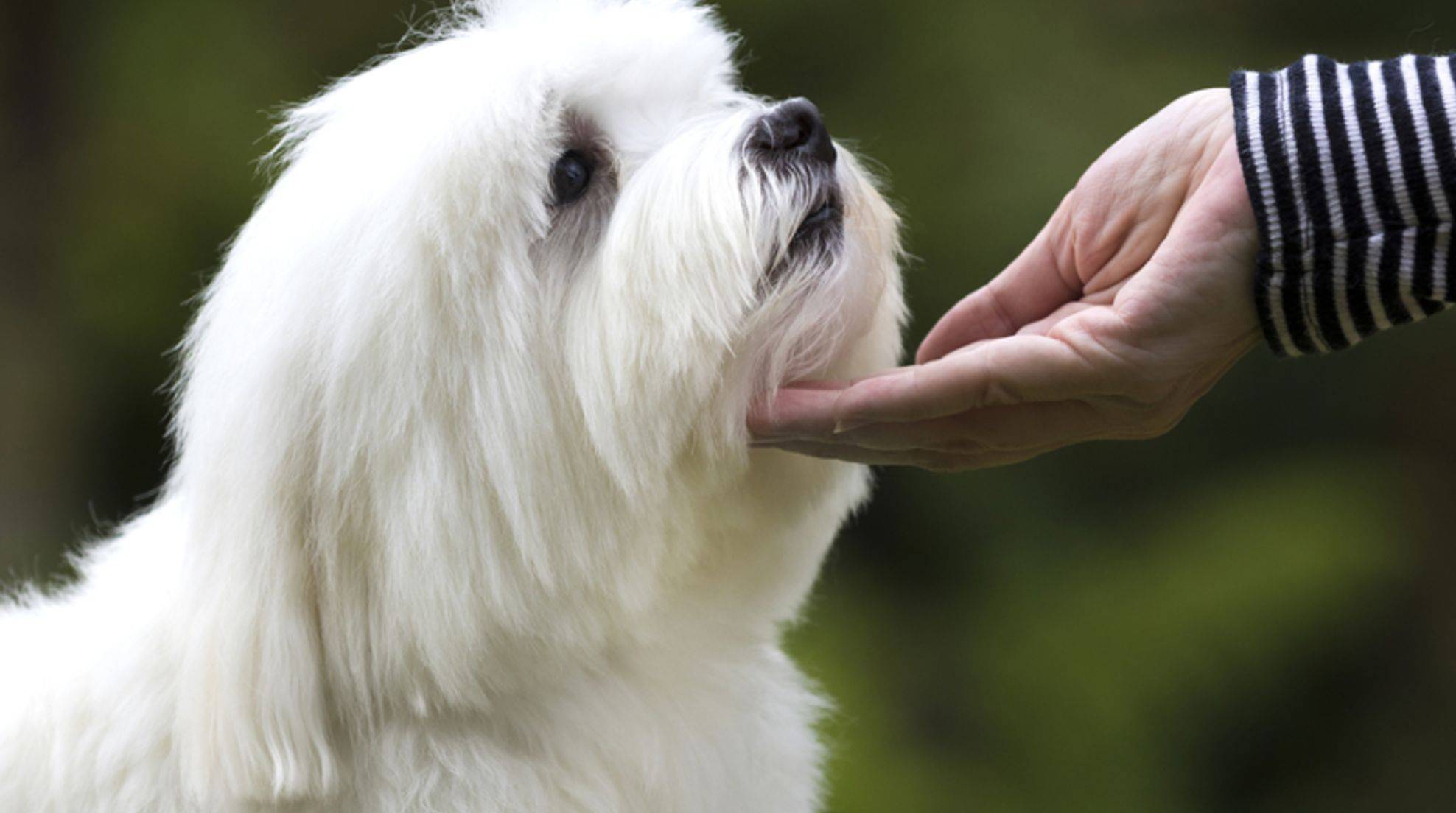
Many dog owners overlook: Dogs also communicate powerfully through their facial expressions. Whether feelings such as hunger, fear, or affection: Your four-legged friend can express many nuances of his emotional world through facial expressions. The dog face’s excellent movements are responsible for the respective facial expressions. Depending on the coat structure and pattern, the effect of the individual words can be intensified.
Beyond that, the dog is above all with the view itself in the position to coin its Mimik crucially. For example, it is a threat if he looks rigidly straight ahead and his pupils are constricted. Dilated pupils and a relaxed face, on the other hand, indicate joy or affection.